Is the effect of the asymmetry between the universal electric field and its corresponding magnetic field – caused by one or more decreased scalars of the Higgs field – significant at the smallest scale size? The question can be answered with the help of the black hole because the difference between a solitary rest mass carrying particle and a black hole is just the size. In other words this post is not about all the details of the properties of black holes, the topic is the supposed creation of consciousness[1] by the asymmetry mentioned above.
Not so long ago the consensus was that black holes are singularities. Personally I don’t understand why theorists had this ridiculous idea. Because quantum field theory exclude this kind of hypotheses that are the result of extrapolations of the properties of an emergent force (gravity). However, the “visible” properties of black holes don’t differ much from other celestial bodies, like heavy planets, stars and neutron stars. All these phenomena show – under certain conditions – accretion disks and (rudimentary) jets. So it is reasonable to think about a black hole as the most dense concentration of energy at the macroscopic scale size.
The consequence is that within the boundary of a black hole all the scalars of the Higgs field are decreased scalars. Therefore there are no 1D vectors to be find within its boundary. Nevertheless, every concentration of energy is forced to rotate because every change of a unit of quantised space during the constant of time (1 tq) has the speed of light. That is why every black hole has a steady rotation.[2] Figure 1 shows a black hole, the resultant vectors of the Higgs field in vacuum space (red arrows), the increasing deformed units by the vectorisation of vacuum space around the black hole (rasterised concentric shells) and of course the schematic units of quantised space. I have drawn these units really large because of the scalar vectors. And… to create “scale correspondence” with rest mass carrying particles.[3]
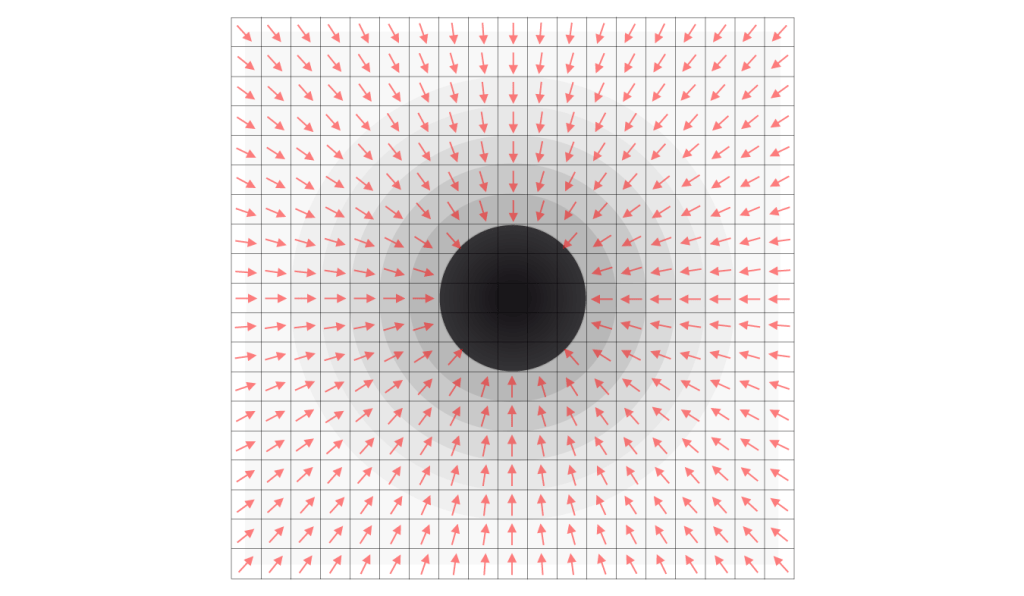
figure 1
The force that is responsible for the creation of energy concentrations is the scalar mechanism of every unit. However, the decrease of 1 or more scalars of the Higgs field creates the vectorisation of the flat Higgs field around matter (red arrows). The consequence is that the vectorisation of the flat Higgs field around the black hole – inclusive the increasing deformation of the universal electric field towards the black hole – is an indissoluble part of the black hole.
The relational properties of the units of quantised space are known as the basic quantum fields in quantum field theory. These properties create “our” phenomenological reality and the consequence is that the structure of quantised space is the rest frame. So if we look at figure 1 we can imagine that the units are in rest and all the topological deformation – inclusive the resultant vectors (red) – are propagated in a certain direction. The cause behind the propagation is not a previous “action”, its cause is the scalar mechanism of all the units in the whole universe (non-local reality).
But if the black hole moves to the top of figure 1 all the units above the black hole are forced to deform more and more, inclusive the vectors of the corresponding magnetic field. While the units at the other side of the black will decrease their high amount of topological deformation during the propagation of the black hole in relation to the rest frame. Figure 2 shows the effect of the “push” of the black hole in the direction of the arrow in relation of the units in vacuum space around the black hole (the rest frame).

figure 2
In other words, the units in the red rasterised part are forced to increase their topological deformation, the units in the blue part decrease the deformation and in between is a neutral zone (transitional zone). This transitional zone is at right angles in respect to the direction of the motion of the black hole. In other words, the drawn vectors are the corresponding vectors of the magnetic field, created by the topological deformation of all the involved units under influence of the propagation of the black hole in vacuum space. Of course the topological deformation of the black hole itself is also propagated by the units of quantised space.
I can combine figure 1 and figure 2 and the result is figure 3. The image shows that the main vector direction in the transition zone is towards the black hole. That means that there is not much turbulence in relation to the “orbiting” quanta of the universal electric field. So it is clear why celestial bodies show accretion disks perpendicular to the direction of the motion of these bodies. Above and below the neutral transition zone there is no stable “orbit” possible (see the red and black vectors in figure 3).
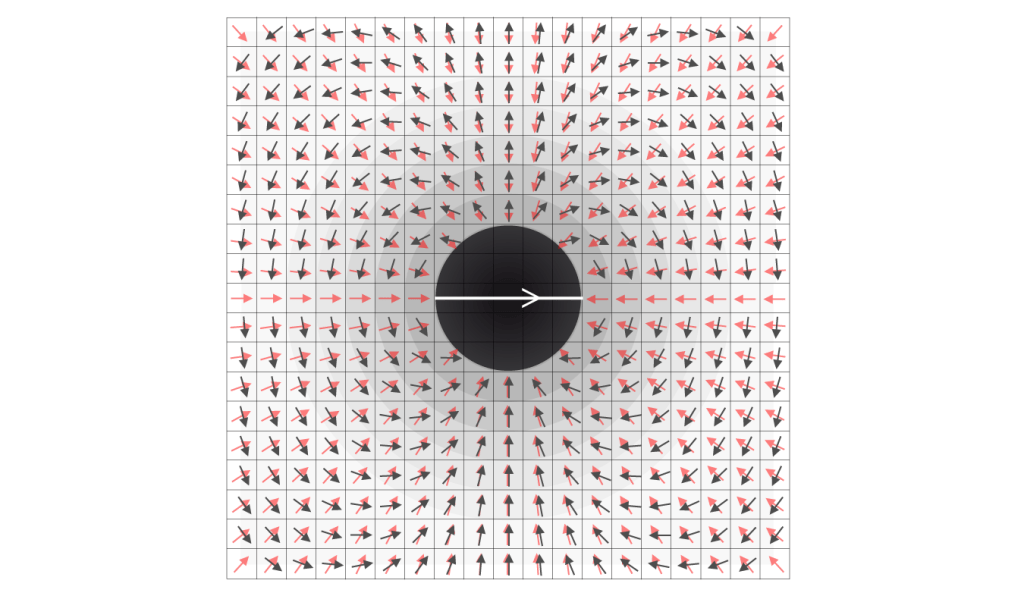
figure 3
Within the boundary of the black hole – created by the vectorised Higgs field around (gravity) – there are no vectors because within the volume of the black hole all scalars are decreased scalars. That means that there are no points of contact between these scalars. As a result these scalars cannot mediate vectors.
However, all the units inside the black hole are much, much more deformed as the units in vacuum space around the black hole. That means that inside the black hole all the topological deformation is created the universal electric field (deformable part of the units). But the deformation doesn’t originate from inside, the deformation – the push – is created by an enormous amount of units around the black hole. Units that try to transfer a bit of their topological deformation to the centre of the concentration of deformation (the black hole). And last but not least, the created dipole by the motion of the black hole in relation to the rest frame – figure 2 – is also “attached” to the propagating black hole in vacuum space.
It is for sure that all the topological deformation in figure 3 – inclusive the black hole itself – doesn’t violate the invariant volume of the units. But the magnitude of the vectorised scalars in vacuum space at the boundary of the black hole – figure 1 – cannot increase because the limit for every unit is just at “the inner edge” of the red line in figure 4. In other words, if the black hole is forced to accumulate more mass – decreasing the radii of the enclosed scalars even further – the magnitude of the vectorisation of the Higgs field itself doesn’t change. Only the amount of decreased scalars will grow.
The further increase of the “push” by all the units around the black hole is the scalar mechanism of the involved units around. That means that the gravitational force is a composition of the vectorisation of the flat Higgs field because of decreased scalars and the further push by the universal electric field towards the centre of the concentration. A push that creates corresponding vectors of the magnetic field in vacuum space towards the black hole. Actually the vectors towards the black hole (red arrows in figure 1) represent a superposition of gravitational vectors and vectors of the magnetic field, generated by the topological deformation of the units in vacuum space around the black hole (electric field). But both type of vectors stop at the boundary of the black hole.

figure 4
If energy is so much concentrated that one of more scalars decrease their radius, the involved decreased scalars stop mediating vectors. The created asymmetry between the points of contact of the scalars around the decreased scalars creates the vectorisation of the Higgs field around. That means that the total magnitude of the vectorisation of the flat Higgs field around is equal to the resistance against topological deformation of the not decreased scalar (red line in the diagram of figure 4). But the concentration of topological deformation has consequences (see figure 5).
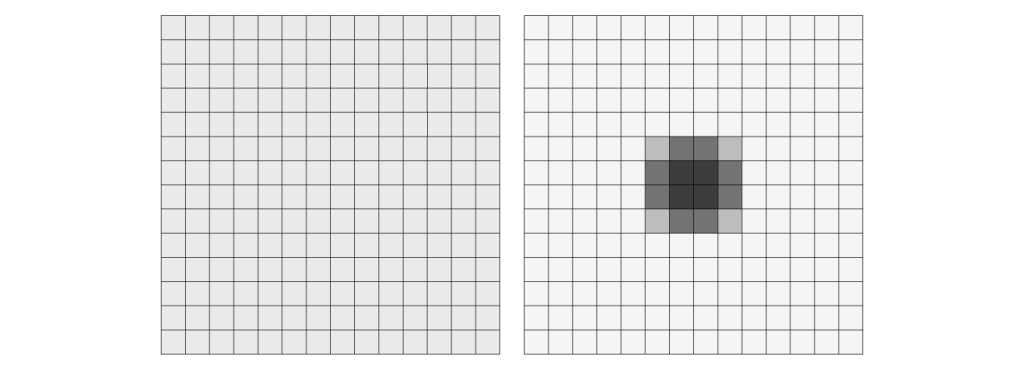
figure 5
The left image and the right image have exactly the same amount of grey. Because the percentage black in each square of the right image is decreased with 1 point and the surplus is added to the units in the centre (like the law of conservation of energy).
So if energy is concentrated the amount of topological deformation of the units around decreases and therefore also the magnitude of the corresponding vectors of the magnetic field. It is reasonable to assume that at the moment a scalar is forced to decrease its radius the total magnitude of the vectorised flat Higgs field is equal to the total magnitude of the vectors of the involved units that point in the direction of the centre of the concentration of energy. Unfortunately every concentration of energy creates a circular transfer of topological deformation around the energy concentration. See figure 6.
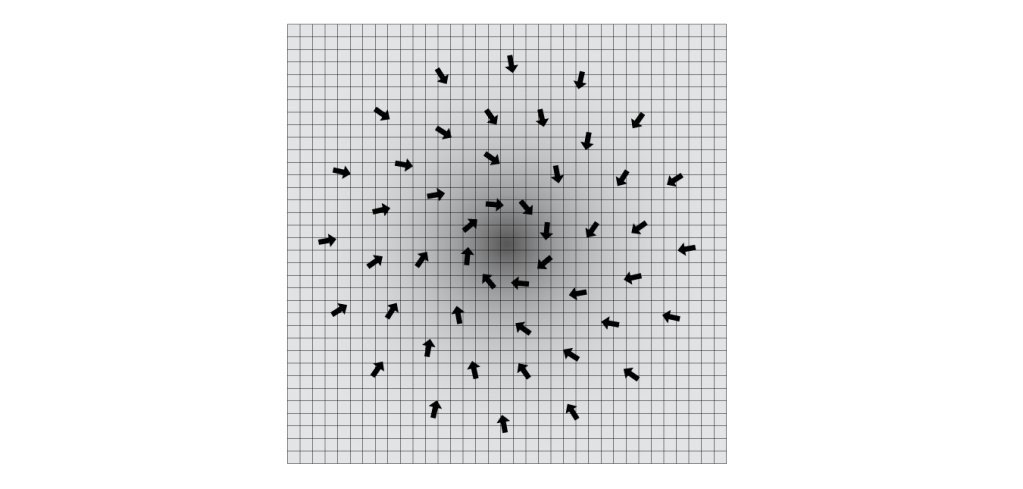
figure 6
The consequence is that the vectors of the magnetic field towards the centre of the concentration of topological deformation don’t represent all the corresponding vectors. Because a part of all the vectors are aligned (“pointing”) around the concentration. Not only affecting the “freedom to deform in every direction”[2] of the units in vacuum space but also affecting the magnitude distribution of the units. Because the total corresponding magnitude of the vectors of every unit in vacuum space during 1 tq (constant of quantum time) is ½ h.
So effectively the increase of a “rotational” propagation of energy decreases the magnitude of the vectors of the magnetic field pointing towards the centre of a concentration of energy. In other words, an increase of mass results in a decrease of the corresponding influence of the magnetic field in the direction of the mass. And we can observe and detect this huge propagation of rotational energy around a concentration of matter in phenomenological reality. Like the creation of a protostar from a huge cloud of dust (figure 7). The white dotted line is to accentuate the existence and position of the protoplanetary disk.
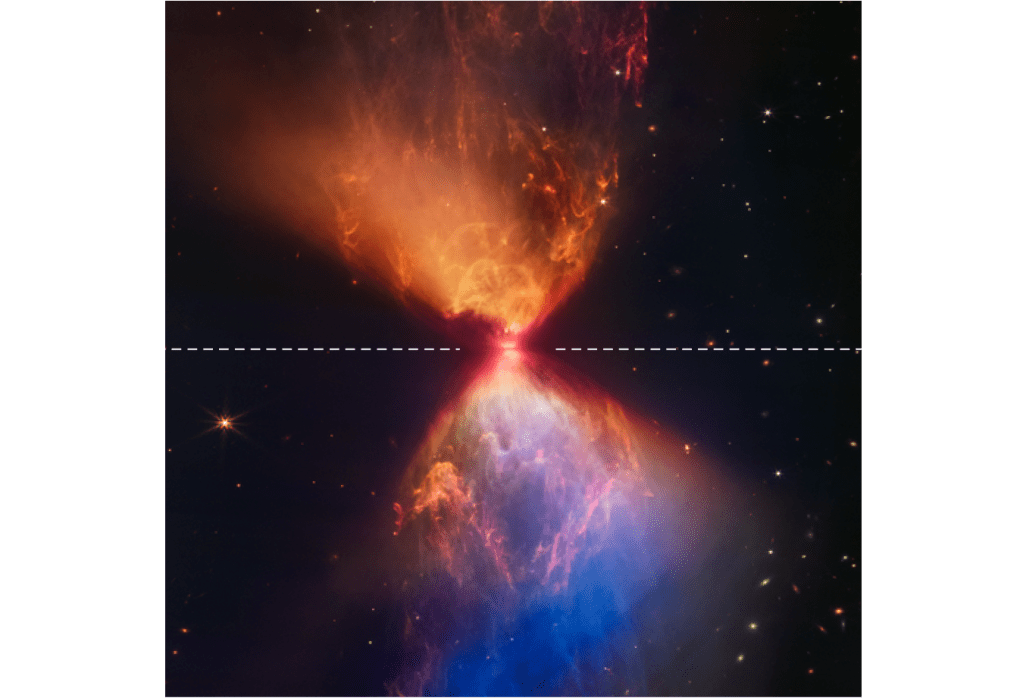
figure 7
The existence of the rotational propagation of energy around matter shows the asymmetry between the local density of the universal electric field in relation to the amount of concentrated energy. Because if a lot of dust (matter) is propagated towards a black hole the velocity of the dust particles nears the speed of light and the result is the emission of electromagnetic radiation. That is why we are aware of the existence of the accretion disk and the 2 jets in line with the rotation axis of the black hole. But without the in-falling dust the accretion disk and the 2 jets still exist “unchanged” although these phenomena of rotational propagation of energy don’t emit electromagnetic radiation.
Conclusion
Every concentration of energy creates rotational propagation of energy in vacuum space. The concentration of energy (rest mass) creates also a dipole of vectors of the magnetic field because of the propagation of the rest mass in relation to the rest frame (figure 2). Not only in the macrocosm but also in the microcosm. Both mechanism will create all kinds of mutual interferences (“relative stable turbulences”) in vacuum space that seem to be “decoupled” from the concentration of energy itself (e.g. the black hole). However, these influences create the conditions but don’t clarify the experience of being a local consciousness.
References:
- (2024); “Consciousness in discrete space”
https://zenodo.org/record/14062564 - (2024); “On resultant motion in discrete space”
https://zenodo.org/record/11193931 - (2019); “On quantum gravity”
https://zenodo.org/record/3590404